A Complete Guide to Building Scalable Test Selenium Automation Framework
An ideal folder structure for a robust Selenium framework that incorporates TestNG, config.properties, POM (Page Object Model), test scripts, Log4j2, Jenkins, and Extent Reports:
Key Components:
Base:
- BaseTest.java: Contains common setup (e.g., browser initialization, teardown, and test configurations).
- DriverManager.java: Handles WebDriver instantiation and lifecycle.
POM (Page Object Model):
- Classes under pages/ encapsulate UI interactions for specific web pages.
Utilities:
- ConfigReader.java: Reads configurations from config.properties.
- LogUtil.java: Sets up Log4j2 for logging.
- ExcelUtil.java: Handles Excel-based test data.
Test Scripts:
- Scripts under tests/ test various functionalities using TestNG annotations.
Reports:
- Generates Extent Reports in reports/ directory with logs and screenshots.
TestNG:
- Centralized configuration (testng.xml) to manage test execution.
Log4j2:
- Logging configurations in log4j2.xml.
Jenkins:
- Pipeline automation managed via Jenkins file.
Example Files:
1. config.properties
- This file contains your configuration, like browser settings, base URLs, etc.
2. log4j2.xml
- Configure Log4j2 for logging. This will log messages to app.log.
3. BaseTest.java
- This is a base class for managing WebDriver setup and teardown.
4. DriverManager.java
- Handles WebDriver initialization.
5. LoginPage.java
- Page Object Model class representing the login page.
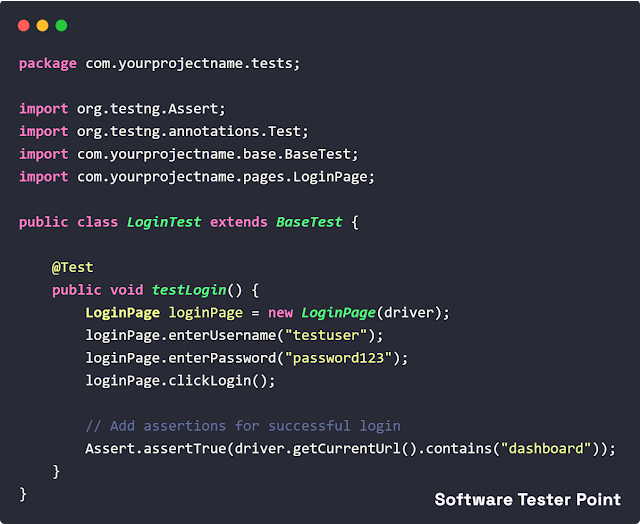
6. LoginTest.java
- Test class using TestNG annotations.
7. testng.xml
- TestNG configuration file to specify test suite and browser parameter.
8. Jenkinsfile
- Jenkins pipeline file for CI/CD automation.
9. Next Steps
- Test Data: Add test data in TestData.xlsx for data-driven tests.
- Jenkins: Set up Jenkins to automate test execution on your repository.
- Reports: Generate detailed test reports using Extent Reports in the reports/ folder.
10. pom.xml (Maven configuration)
The pom.xml file is essential for managing dependencies, building the project, and running tests. Below is an example of a pom.xml that includes dependencies for Selenium, TestNG, Log4j2, ExtentReports, and other utilities.
- Selenium WebDriver: The dependency for Selenium WebDriver to interact with browsers.
- TestNG: Dependency for running tests in parallel and managing test cases.
- Log4j2: Used for logging the test execution.
- ExtentReports: Provides rich test reports with screenshots, logs, and other details.
- WebDriverManager: Automatically manages browser drivers, making it easier to set up WebDriver.
- Apache POI: For reading and writing Excel files (if you're doing data-driven testing).
11. testng.xml (TestNG configuration)
The testng.xml file is used to configure and control the execution of TestNG tests. Below is an example of a testng.xml file.
- parallel: Defines the parallelism strategy for executing tests (in this case, tests are run in parallel).
- thread-count: Defines how many threads to run simultaneously.
- test: Defines individual tests (e.g., LoginTest, DashboardTest).
- parameter: Allows you to pass parameters (like browser) to the test methods.
How to Run Tests:
Run Tests Using Maven:
- Open terminal and navigate to your project directory.
- Run the following command to execute tests using TestNG
Run Tests Using Jenkins:
- The Jenkins Jenkinsfile will use this pom.xml to install dependencies and run the tests. Jenkins will trigger the testng.xml file for the test execution.